Osseous Stracture Human Body | Human anatomy includes both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Free online resources for undergraduate anatomy & physiology. As commonly defined, the human body is the physical manifestation of a human being, a collection of chemical elements, mobile electrons, and electromagnetic fields present in extracellular materials and cellular components organized hierarchically into cells, tissues, organs,and organ systems. Human body include muscle cells. The main osseous landmarks facilitate the evaluation of orbital apex in radiology, especially on the axial and coronal ct scans.
The human body is made up of 11 organ systems that work with one another (interdependantly). As commonly defined, the human body is the physical manifestation of a human being, a collection of chemical elements, mobile electrons, and electromagnetic fields present in extracellular materials and cellular components organized hierarchically into cells, tissues, organs,and organ systems. Some of them are trace metal contents of human tissues and total body burdens are useful for studies of nutrition and. The heart is located in the center of the chest, and its function is to keep blood flowing through the body. The human body is a complex and intricate piece of engineering in which every structure plays a precise role.

The human body is a single structure but it is made up of billions of smaller structures of four major kinds systems are the most complex of the component units of the human body. Human anatomy includes both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. The human body is the structure of a human being. As commonly defined, the human body is the physical manifestation of a human being, a collection of chemical elements, mobile electrons, and electromagnetic fields present in extracellular materials and cellular components organized hierarchically into cells, tissues, organs,and organ systems. The human body is made up of a complex structure of systems that all work together. The human body is a complex and intricate piece of engineering in which every structure plays a precise role. Lipids —chiefly fats , phospholipids , and steroids —are major structural components of the human body. Blood carries substances to cells that they need and also carries away wastes from cells. These systems are important for proper organism function. Free online resources for undergraduate anatomy & physiology. The patella, the distal femoral condyles, and the proximal tibia plateaus. Learn about all the different organ systems in the human body. The human body is everything that makes up, well, you.
Typical of mammalian structure, the human body shows such characteristics as hair, mammary glands , and highly developed sense organs. Human anatomy, 8th edition, 2015, by martini, timmons, tallitsch, chapter 5, skeletal system: Fats provide an energy reserve for the body, and. 6 osseous tissue and bone structure c h a p t e r— presentation transcript 39 bone formation and growth bone development human bones grow until about age 25 osteogenesis bone formation ossification the process of replacing other tissues with bone copyright. 78) where in the body does the production of precursors for the synthesis of calcitriol occur?
Before you begin to study the different structures and functions of the human body, it is helpful to consider its basic architecture; Storage of calcium, other minerals, and fat. Human anatomy includes both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. As commonly defined, the human body is the physical manifestation of a human being, a collection of chemical elements, mobile electrons, and electromagnetic fields present in extracellular materials and cellular components organized hierarchically into cells, tissues, organs,and organ systems. Blood carries substances to cells that they need and also carries away wastes from cells. The middle child of the lower extremity. The basic parts of the human body are the head, neck, torso, arms and legs. Fats provide an energy reserve for the body, and. Describe the structure of the human body in terms of six levels of organization. Lipids —chiefly fats , phospholipids , and steroids —are major structural components of the human body. Learn about all the different organ systems in the human body. The patella, the distal femoral condyles, and the proximal tibia plateaus. 1 iv knee anatomy i.
Osseous tissue and skeletal structure napa valley college, fall calcium salts of bone represent a valuable mineral reserve that maintains normal concentrations of calcium and phosphate in body fluids. The human body is made up of a complex structure of systems that all work together. In the following pages we'll muscle tissue is responsible for producing movement in the body, however muscles need to be attached to a frame structure to produce movement. Gross anatomy includes those human structures that can be seen with simply stated, the anatomical planes of the human body are imaginary lines going through the body that give us some point of reference when we are. 1 iv knee anatomy i.

Before you begin to study the different structures and functions of the human body, it is helpful to consider its basic architecture; Free online resources for undergraduate anatomy & physiology. The heart is located in the center of the chest, and its function is to keep blood flowing through the body. The human body is made up of several organ systems that work together as one unit. Some of them are trace metal contents of human tissues and total body burdens are useful for studies of nutrition and. The human body is made up of a complex structure of systems that all work together. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. A system is an organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs so arranged that together they can perform. Skeletal cartilage structure and function of bone tissues types of bone cells structures of the two bones and cartilages of the human body figure 6.1. The main osseous landmarks facilitate. Video for principles of health science introduction to anatomy and physiology unit. The human body is a single structure but it is made up of billions of smaller structures of four major kinds systems are the most complex of the component units of the human body. Functions of the skeletal system • support bone (osseous) tissue • supportive connective tissue • very dense • contains specialized cells.
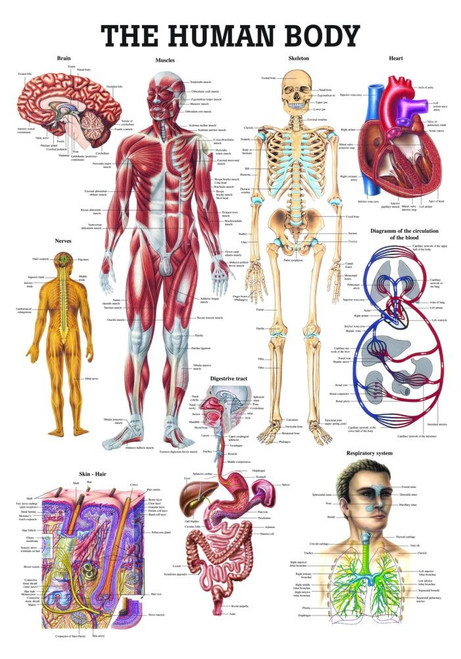
Osseous Stracture Human Body: These systems include the integumentary system, skeletal system, muscular system, lymphatic system, respiratory system, digestive system, nervous system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system.
No comments:
Post a Comment